Deepdive
(Advertisement)
What are DAOs and How Do They Work?

Learn everything about Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): how they work, how to join them, and why they're revolutionizing organizational structure in the blockchain era.
Crypto Rich
February 4, 2025
(Advertisement)
Table of Contents
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent one of the most innovative applications of blockchain technology, fundamentally changing how organizations can be structured and governed in the digital age. These member-owned communities operate without centralized leadership, instead relying on smart contracts and blockchain technology to enforce rules, execute decisions, and manage resources transparently.
Understanding DAOs: The Basics
At its core, a DAO is a blockchain-based organization that operates according to rules encoded as computer programs, transparent and unalterable by any single party. Unlike traditional organizations with hierarchical management structures, DAOs implement an automated decision-making process where members collectively make choices about the organization's future.
These digital organizations eliminate the need for conventional management hierarchies, replacing them with incentive systems that automatically execute when specific conditions are met. This revolutionary approach to organizational structure promotes transparency, reduces operational costs, and minimizes the risk of human error or manipulation.

How DAOs Function in Practice
DAOs operate through smart contracts – self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code. These smart contracts establish the fundamental rules and execute the agreed-upon decisions. The process typically works as follows:
- Creation and Rules: First, developers create the smart contracts that establish the DAO's rules
- Funding: The DAO receives funding through token issuance
- Deployment: Once deployed, the DAO's code cannot be changed except through member voting
- Proposals and Voting: Members submit proposals and vote on various initiatives
The entire process is transparent, with all rules and financial transactions recorded on the blockchain, visible to anyone who wishes to examine them.
Gaining Access to DAOs: Membership Models
Token-Based Membership
The most common way to join a DAO is through token-based membership. Users typically gain access by:
- Purchasing governance tokens on decentralized exchanges
- Earning tokens through participation or contribution
- Receiving tokens as rewards for providing liquidity
- Acquiring tokens through initial token offerings
These governance tokens grant voting rights and allow members to influence the DAO's direction proportional to their holdings.
Voting and Governance Platforms
Many DAOs utilize specialized platforms to manage their governance processes. Snapshot has emerged as a leading platform for decentralized voting, allowing DAOs to conduct gasless, off-chain voting. This platform enables organizations to create proposals, vote on important decisions, and manage community governance without incurring blockchain transaction fees.
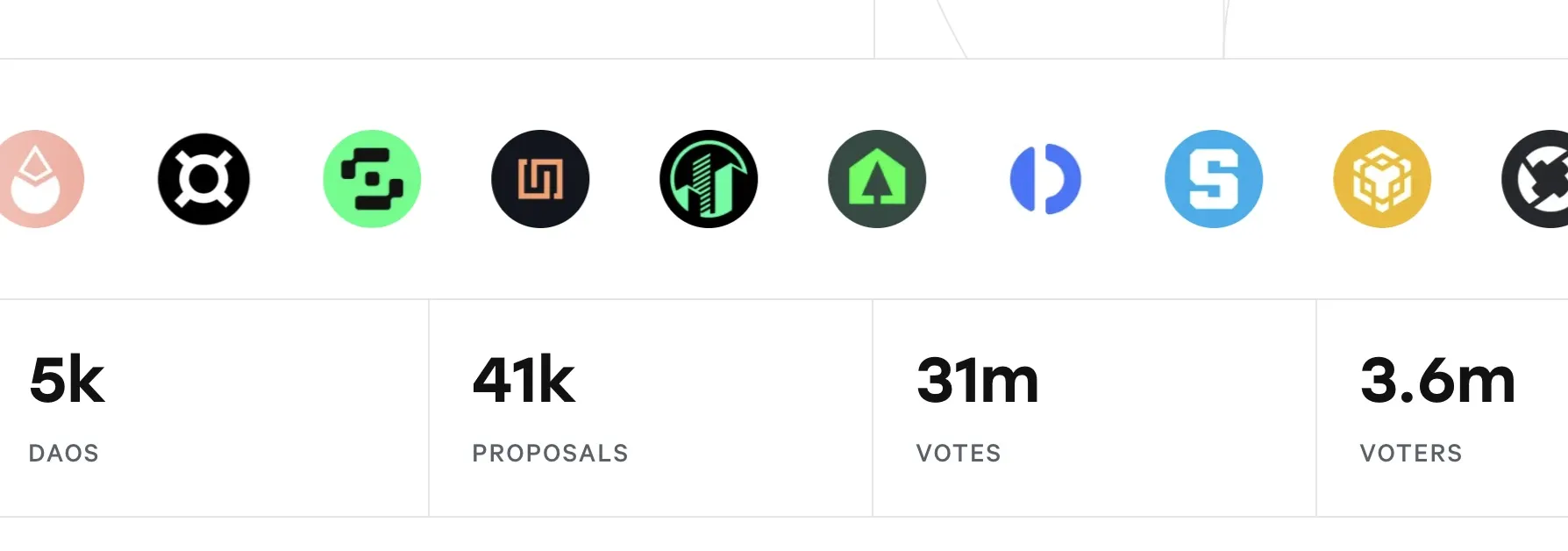
Real-World Applications of DAOs
DAOs have found practical applications across various sectors:
Investment DAOs
Investment DAOs pool member resources to invest in digital assets, NFTs, or even traditional investments. Members collectively decide on investment strategies and share both risks and rewards.
Protocol DAOs
These DAOs govern decentralized protocols, making decisions about parameter changes, upgrades, and resource allocation. Popular examples include Uniswap and Aave.
Social DAOs
Communities formed around shared interests, where members collectively own and manage community resources, content, and activities.
Memecoin DAOs
The DAO concept has even penetrated the world of memecoins, with cryptocurrencies like Floki implementing decentralized governance models. These community-driven projects use DAOs to allow token holders to participate in key decisions, from marketing strategies to project development. For instance, Floki's DAO enables community members to propose and vote on initiatives, demonstrating how all manner of crypto projects are embracing more democratic and transparent governance structures.
This trend highlights the versatility of DAOs, showing they're not limited to dry financial or technical projects but can be applied across various types of digital communities and cryptocurrencies. By giving power directly to token holders, memecoin DAOs create a more engaged and participatory ecosystem that goes beyond traditional top-down management approaches.
Benefits and Challenges of DAOs
Advantages
- Transparent operations with all actions recorded on the blockchain
- Reduced operational costs through automation
- Democratic decision-making processes
- Global accessibility and participation
- Elimination of hierarchical bottlenecks
Potential Challenges
- Smart contract vulnerabilities
- Regulatory uncertainty in many jurisdictions
- Potential for governance attacks through token accumulation
- Coordination challenges in large-scale decision-making
The Future of DAOs
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, DAOs are positioned to play an increasingly important role in organizational structure and governance. Industries from finance to social media are exploring DAO implementations, suggesting a future where decentralized governance becomes more commonplace.
Conclusion
DAOs represent a paradigm shift in how organizations can be structured and managed in the digital age. By combining blockchain technology with democratic governance principles, they offer a new model for collective decision-making and resource management. While challenges remain, the growing adoption of DAOs across various sectors indicates their potential to reshape organizational dynamics in the years to come.
Whether you're a developer, or simply interested in new forms of organization, understanding DAOs is crucial as they continue to influence the future of collective governance and decision-making in the digital world.
Read Next...
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
(Advertisement)
Latest News
(Advertisement)
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens













